Guide to New Construction Homes: Process, Benefits, and Builders

New construction homesare properties built from the ground up. This guide, by Daniel Yoon, Certified New Home Co-Broker, covers the process, benefits, and key considerations for buyers. It explores types of new builds (custom, production, spec, townhomes), compares them with existing homes, and outlines practical steps from planning to move-in. Topics include financing, inspections, community amenities, HOA rules, energy efficiency, and smart home trends for 2024–2025.
What Is New Construction? Defining New Construction Homes and Key Concepts
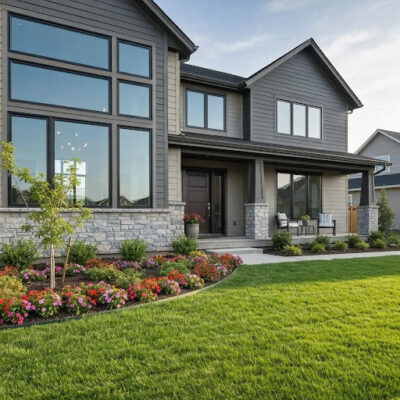
New construction homes are built on new or vacant lots, with all structures, systems, and finishes installed for the first time. This offers customization, modern codes, and warranties, but also introduces scheduling and procurement risks. Understanding these distinctions helps buyers choose between move-in ready, custom, or production homes, and frames expectations for costs and maintenance.
What Are the Main Types of New Construction Homes?
New construction offers several models: custom, production, spec, and townhomes, each suiting different buyer goals and budgets. Custom homes offer unique designs and lot selection but have longer timelines and higher costs. Production homes (tract homes) provide faster timelines and lower costs via standardized plans. Spec homes offer immediate occupancy with limited customization. New townhomes blend density with community amenities. Choose based on desired customization, timeline, and budget.
Types of New Construction Homes
Custom Homes
Unique design, lot selection, longer timelines, higher costs.
Production Homes
Standardized plans, faster timelines, lower costs (tract homes).
Spec Homes
Immediate occupancy, limited customization, builder-chosen finishes.
Townhomes
Blended density, community amenities, shared walls.
How Does New Construction Differ from Existing Homes?
New construction differs from existing homes in age, systems, and code compliance. New builds meet current energy codes with modern HVAC, insulation, and electrical systems, reducing maintenance and utility costs. Existing homes may need upgrades or repairs. While new builds can face timeline uncertainties and supply chain delays, resale homes often close faster but may have hidden maintenance costs. Buyers should compare lifecycle costs, energy performance, and warranty coverage to determine if new construction’s lower maintenance and contemporary systems justify a premium over resale.
What Are the Benefits of Buying a New Construction Home?
New construction homes offer significant benefits: energy efficiency, customization, and warranty protections, reducing maintenance uncertainty and enhancing long-term value. Modern codes and materials lead to lower operating costs. The ability to choose finishes and floor plans aligns the home with lifestyle needs. New home warranties provide structured remedies for workmanship and structural issues, reducing post-closing risk.
Top Benefits of New Construction Homes
Energy Efficiency
Lower utility bills, improved comfort, modern systems.
Customization
Personalized finishes, layouts, and structural options.
Warranty Protections
Structured remedies for workmanship and structural issues.
Modern Safety & Codes
Updated electrical, plumbing, and fire safety systems.
New construction offers several distinct advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: New systems and insulation reduce monthly utility costs and improve comfort.
- Customization: Buyers can select finishes, layouts, and sometimes structural options to match preferences.
- Warranty Protections: Structured workmanship and structural warranties provide recourse for defects.
- Modern Safety and Code Compliance: Updated electrical, plumbing, and fire safety systems align with current standards.
| Feature Category | Typical Element | Expected Buyer Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High performance insulation, modern HVAC, LED lighting | Lower utility bills; improved comfort and air quality |
| Customization | Kitchen finishes, flooring, layout changes | Higher satisfaction and tailored living spaces |
| Warranty Coverage | Workmanship (1–2 yrs), systems (2–5 yrs), structural (10 yrs) | Reduced repair risk and clearer claims process |
| Smart Home Readiness | Pre wiring, smart thermostats, security integration | Easier upgrades and higher resale appeal |
How Do Energy Efficiency and Smart Home Features Add Value?
Energy efficient design and smart home readiness reduce operating costs and boost resale desirability. Efficient HVAC, insulation, and ENERGY STAR appliances lower energy consumption. Smart thermostats, security, and lighting enhance convenience and perceived value. Market trends (2024–2025) show strong buyer interest in homes with lower utility footprints and tech integration, leading to faster resale and stronger appraisals. Understanding these features helps buyers estimate savings and make informed upgrade choices.
What Customization and Warranty Options Are Available?
Buyers face tiered customization, from base finishes to structural changes, which should be weighed against budget and resale. Upgrades like kitchens, flooring, and fixtures have price impacts and deadlines; larger structural changes require negotiation. Warranties typically cover short-term workmanship, intermediate systems, and long-term structural elements. Buyers must document warranty terms, claim procedures, and maintenance obligations to preserve coverage. Written confirmation of upgrades and warranty scope during contract review prevents misunderstandings.
What Is the Step by Step New Construction Process?
The new construction process involves defined phases: planning, permitting, site work, framing, systems installation, finishes, inspections, and final walkthrough, with staged decisions and payment draws. Each phase has buyer responsibilities like selecting finishes and approving plans. Buyers should maintain a clear timeline and contacts. Common delays stem from permitting, weather, and supply chains; proactive communication and contingency planning reduce risk.
New Construction Process Timeline
1. Planning & Design
Budget, floor plan, selections, lender pre-approval.
2. Permitting & Site Work
Obtain permits, clear lot, establish utilities.
3. Construction & Finishes
Framing, systems rough-in, insulation, interior/exterior finishes.
4. Inspections & Walkthrough
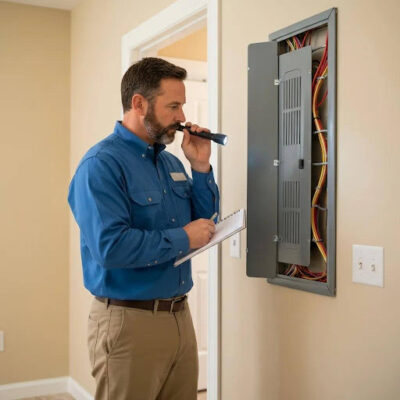

Final inspections, punch list, pre-closing review.
Key phases and buyer checkpoints are:
- Planning & Design: Finalize budget, floor plan, and selections; secure lender pre-approval if needed.
- Permitting & Site Work: Obtain local permits, clear and grade lot, and establish utilities.
- Construction & Finishes: Framing, systems rough-in (electrical/plumbing/HVAC), insulation, then finishes.
- Inspections & Walkthrough: Schedule final inspections and the builder’s punch list walkthrough before closing.
What Are the Key Phases from Planning to Move In?
The journey from planning to move-in typically spans months to over a year, depending on the build type and local conditions, requiring timely buyer input. Planning and design finalize floor plans and budgets. Permitting and site work follow, subject to municipal timelines. Framing and systems installation are visible progress stages, often triggering lender draws. Finishes and inspections finalize the build. Buyers should document selection deadlines, approvals, and change orders. Clear communication with the builder on progress and delays ensures transparency before closing.
How Do You Choose a Reputable New Home Builder?
Choosing a reputable builderrequires objective vetting. Verify licensing, insurance, references, and portfolios. Examine warranty policies and contract clarity, comparing several candidates. Vetting checklists should include confirming local licensing, inspecting model homes, and contacting recent buyers. Also, assess how the builder handles change orders and warranty claims. Red flags include vague timelines, reluctance to provide references, unclear warranty procedures, or contracts lacking detailed scope. Consult builder directories, licensing boards, and consumer protection regulators for independent verification.
How Do You Finance a New Construction Home? Understanding Costs and Loans
Financing new construction involves distinct loan products and budget items: construction only loans, construction to perm loans, draw schedules, and phased interest payments. Construction only loans cover the build period with interest-only payments, requiring separate permanent refinancing. Construction to perm loans convert to a traditional mortgage at completion, simplifying the process. FHA and VA options may also be available. Understanding draw schedules, down payment expectations, and how incentives affect closing costs is crucial for budgeting.
Introductory list of financing considerations:
- Construction Loan Type: Determine whether construction only or construction to perm suits your timeline and refinancing tolerance.
- Down Payment & Reserves: Expect different down payment requirements and documentation compared with conventional mortgages.
- Draw Schedule & Inspections: Funds are released at milestones based on inspections and lien waivers.
- Conversion & Rates: Clarify how and when interest rates convert and whether there is a rate lock for the permanent mortgage.
| Loan Type | Typical Down Payment | Interest / Term Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Only | 20%–25% | Interest only during build; permanent refinancing required |
| Construction to Perm | 10%–25% | Single close loan; converts to mortgage at completion |
| FHA/VA Construction Programs | Varies by program | Program specific protections; conversion options available |
What Financing Options and Construction Loans Are Available?
Construction only loans are short-term, financing building costs with interest-only payments during construction, requiring a separate permanent mortgage later, which adds refinancing risk. Construction to perm loans offer a single close solution, converting to a conventional mortgage upon completion, simplifying financing and often reducing fees. FHA and VA construction programs, available in some areas, can lower down payment barriers but have specific requirements. When comparing offers, evaluate rates, conversion mechanics, lender experience with draws, required inspections, and fees to minimize total cost and risk.
How Do Builder Incentives and Closing Costs Affect Your Budget?
Builder incentives (upgrade credits, closing cost contributions, rate buydowns) can reduce upfront cash but may impact net purchase price or appraisal. New build specific closing costs include impact fees, utility hookups, and initial HOA setup; factor these into your budget. Negotiate incentives by clarifying if credits are seller concessions or upgrade allowances, and understand their impact on loan type limits. Use a closing cost worksheet and compare lender fee estimates to accurately assess out-of-pocket expenses.
What Should You Know About New Home Inspections and Warranties?
Effective inspection timing and a clear warranty strategy are crucial for buyers during handover and early ownership. Inspections occur at rough-in and final completion, leading to a punch list of issues for correction. Warranties typically cover short-term workmanship, intermediate systems, and long-term structural elements. Understanding warranty lengths, claim procedures, and maintenance obligations is vital for preserving coverage.
Introductory inspection checklist overview: priority areas to inspect and document during walkthroughs.
- Exterior & Site: Check grading, drainage, roofing, and exterior finishes for defects.
- Systems & Utilities: Verify HVAC, plumbing, electrical, and hot water systems function properly.
- Interior Finishes: Inspect doors, windows, flooring, cabinetry, and paint for defects.
- Safety & Compliance: Confirm smoke detectors, GFCI outlets, and code-related safety items.
Use photographic documentation and dated notes during each checklist item to build an actionable punch list.
| Warranty Type | Typical Coverage | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Workmanship | Cosmetic and contractor installed items | 1–2 years |
| Systems | HVAC, plumbing, electrical systems | 2–5 years |
| Structural | Load bearing elements, foundation | Up to 10 years |
How to Conduct Effective New Home Inspections and Walkthroughs?
Conduct inspections in stages: rough-in, pre-drywall, and final walkthrough, documenting issues with photos, notes, and time-stamped records for punch list resolution. Hire an independent inspector experienced in new construction to evaluate systems and quality, complementing builder self-inspections. During the final walkthrough, prioritize safety and major systems, then catalog cosmetic items by room and urgency for a prioritized punch list. Submit the punch list in writing, request correction dates, and retain communication copies to ensure timely responses and preserve warranty remedies.
What Do New Home Warranties Cover and How Do They Protect You?
New home warranties define responsibilities among builders, subcontractors, and manufacturers, covering workmanship defects, system failures, and structural deficiencies for varying timeframes. Structural warranties address major load-bearing failures (longest duration), systems warranties target mechanical failures, and workmanship warranties cover aesthetic or minor installation defects. Buyers must understand claim procedures, required maintenance to preserve coverage. Maintaining records and adhering to service schedules are crucial for successful claims. These distinctions help buyers prioritize inspections and negotiate warranty enforcement clarity in the contract.
New Home Warranty Breakdown
Workmanship Warranty
Covers cosmetic and installation defects. Typical Duration: 1-2 Years
Systems Warranty
Covers HVAC, plumbing, electrical systems. Typical Duration: 2-5 Years
Structural Warranty
Covers major load-bearing elements, foundation. Typical Duration: Up to 10 Years
What Are the Features and Amenities of New Home Communities?
New home communities often feature amenities like parks, pools, clubhouses, and trails, impacting HOA fees, lifestyle, and resale value. Buyers should assess if recurring costs align with perceived benefits. Amenities enhance community cohesion and attract specific buyers but also incur maintenance and reserve funding needs, affecting monthly HOA dues. Review HOA covenants and budgets for fee escalation and capital plans. Request financial statements and rules on exterior modifications or rental proportions.
| Amenity | Typical HOA Impact | Buyer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pool/Clubhouse | Moderate–High dues; seasonal maintenance | Recreation, social hub, resale appeal |
| Trails & Parks | Low–Moderate dues; landscaping | Outdoor access, family friendly environment |
| Fitness Center | Moderate dues; equipment upkeep | Convenience, health focused amenity |
| Community Events | Minor fees; administrative costs | Social cohesion, neighborhood culture |
How Do Community Amenities Enhance New Construction Living?
Amenities expand lifestyle options and influence resale by attracting specific buyer segments (e.g., families, professionals). Well-maintained amenities boost desirability and support higher resale comparables. Buyers should weigh the net present value of amenities against monthly HOA contributions and potential special assessments. Consider developer management initially and how control transitions to the HOA, as operating models may change. Evaluating amenity usage and funding helps determine alignment with needs and long-term property value.
What Role Do HOAs and Local Regulations Play in New Developments?
HOAs and local zoning regulations dictate property modifications, maintenance, and fee structures, impacting customization and future development. Review HOA CC&Rs for limits on exterior alterations, rental rules, and landscaping. Note fee escalation clauses and reserve fund health to anticipate assessments. Local regulations (setbacks, density, commercial uses) shape neighborhood character and may signal future development affecting resale. Check municipal permit records and zoning maps for regulatory constraints and planned projects.
Schedule independent inspection support, consult local building regulators for permit histories, and engage a mortgage advisor experienced in construction financing. This resource equips buyers with practical tools and negotiation points. For deeper, downloadable checklists, seek authoritative industry resources and local regulatory guidance tailored to your market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common challenges faced during the new construction process?
Challenges include delays from permitting, weather, and supply chain issues, plus unexpected costs for site prep or material changes. Communication gaps can also cause misunderstandings. Mitigate these by maintaining proactive communication with builders, staying informed on schedules, and having contingency plans for delays or budget overruns.
How can buyers ensure they are making a sound investment in new construction?
Ensure a sound investment by researching the builder’s reputation, reviewing past projects, and seeking client references. Understand local real estate market trends and evaluate long-term benefits like energy efficiency and modern amenities for resale value. Consult real estate professionals and financial advisors for informed decisions aligned with investment goals.
What should buyers know about energy efficiency ratings and certifications?
Energy efficiency ratings (e.g., ENERGY STAR, LEED) indicate a home’s energy consumption and environmental impact. Certified homes feature high-quality insulation, efficient appliances, and advanced HVAC, leading to lower utility bills and increased comfort. Buyers should inquire about specific features and how ratings affect long-term savings and resale value, making informed choices aligned with sustainability goals.
What are the implications of community regulations on new construction homes?
Community regulations, including zoning laws and HOA rules, significantly impact new construction. They dictate property modifications, maintenance, and standards, affecting customization. Buyers must review HOA covenants and zoning regulations for restrictions on exterior changes, rental policies, and landscaping. Awareness helps avoid conflicts, ensures compliance, and protects investment.
How do market trends influence the decision to buy new construction homes?
Market trends, including interest rates, housing supply, and buyer demand, critically influence new construction decisions, affecting pricing and availability. In competitive markets, new builds offer advantages like modern amenities and energy efficiency. Understanding local development trends (e.g., new schools, commercial projects) can indicate future property value appreciation. Buyers should stay informed to make strategic decisions aligned with long-term housing goals.
What financing options are available specifically for new construction homes?
New construction financing differs from traditional mortgages, offering construction only loans, construction to permanent loans, and FHA/VA programs. Construction only loans cover the build phase, requiring a separate permanent mortgage. Construction to permanent loans convert to a traditional mortgage upon completion. Buyers should evaluate terms, down payment requirements, and interest rates to find the best fit for their financial situation and project timeline.
Conclusion
Investing in a new construction home provides significant advantages: energy efficiency, customization, and robust warranty protections, enhancing long-term value. This guide equips buyers with essential knowledge on the construction process, financing, and community considerations for informed decisions. Consult industry experts and access valuable tools to begin your new home adventure today.